
Given two independent events, if the first event can yield one of n equiprobable outcomes and another has one of m equiprobable outcomes then there are mn equiprobable outcomes of the joint event.\text. p 2) = I( p 1) + I( p 2): the information learned from independent events is the sum of the information learned from each event.All spontaneous change occurs with an increase in entropy of the universe. The universe tends toward increased entropy. A positive (+) entropy change means an increase in disorder. I(1) = 0: events that always occur do not communicate information. Entropy, S, is a state function and is a measure of disorder or randomness.If an amount of heat dQ flows from system to the surroundings. Heat transfer will take place between the system and surroundings. Entropy change in an irreversible process: Consider the system and surroundings at different temperatures T1 and T2 respectively with T1 > T2. So part of the entropy per molecule is evidently Boltzmanns constant kB.
In both cases, you would observe how the systems performance changes (or doesnt change) after you. I( p) is monotonically decreasing in p: an increase in the probability of an event decreases the information from an observed event, and vice versa. The second law of thermodynamics is best expressed in terms of a change in the thermodynamic variable known as entropy, which is represented by the symbol S.Entropy, like internal energy, is a state function. Change of entropy of an adiabatic process is zero. On doubling the volume, there is an entropy increase of kBln2 per molecule. Processes or techniques, such as a data preprocessing step.The amount of information acquired due to the observation of event i follows from Shannon's solution of the fundamental properties of information: To understand the meaning of −Σ p i log( p i), first define an information function I in terms of an event i with probability p i. The greater the value of entropy, H(x), the greater the uncertainty for probability distribution and the smaller the value the less the uncertainty.
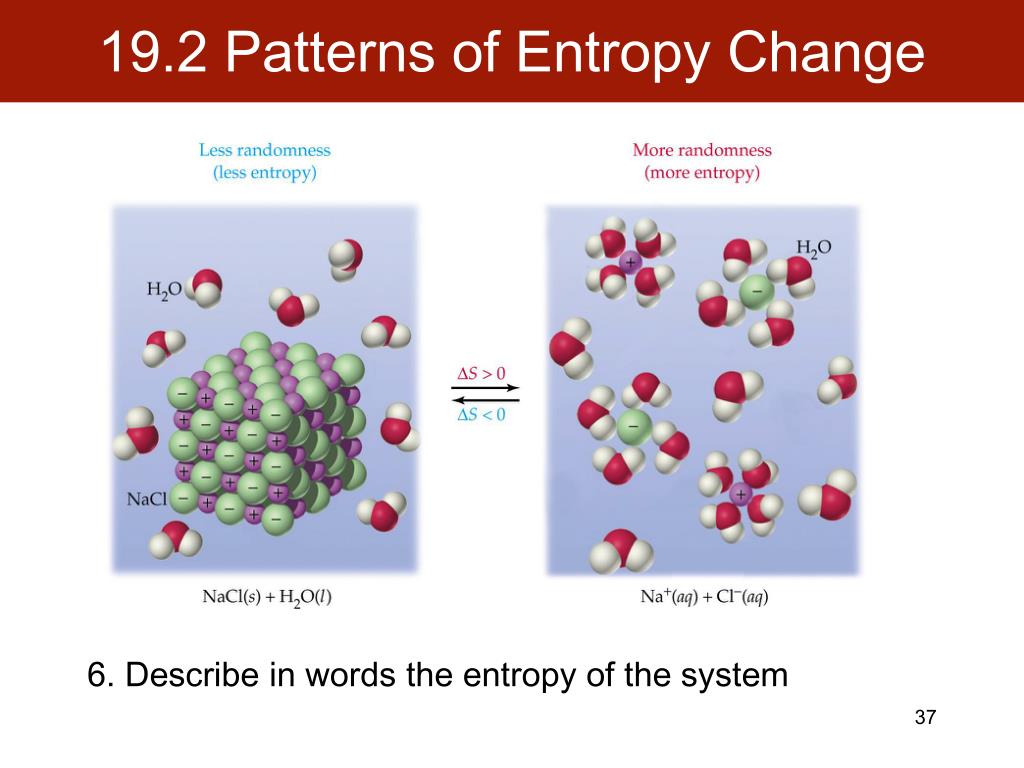
A reduction in 'chaos' is reduction of entropy, such as when you sort the m&m's in colors, but another part of the system must have an increase in entropy in order for you to do. The entropy is zero: each toss of the coin delivers no new information as the outcome of each coin toss is always certain. Given prior knowledge of the thermodynamic terms entropy, enthalpy, and spontaneous processes, students will gain a deeper understanding of how G Hsys T. \begingroup If the entropy change is negative for one part of a system, it must be positive for another, in order to still fulfill the requirement you have shown. But all real processes are irreversible, thus Stot > 0 S t o t > 0. Total entropy is not a conserved quantity, except in the ideal case of a reversible process in which case Stot 0 S t o t 0.
CHANGE IN ENTROPY PLUS
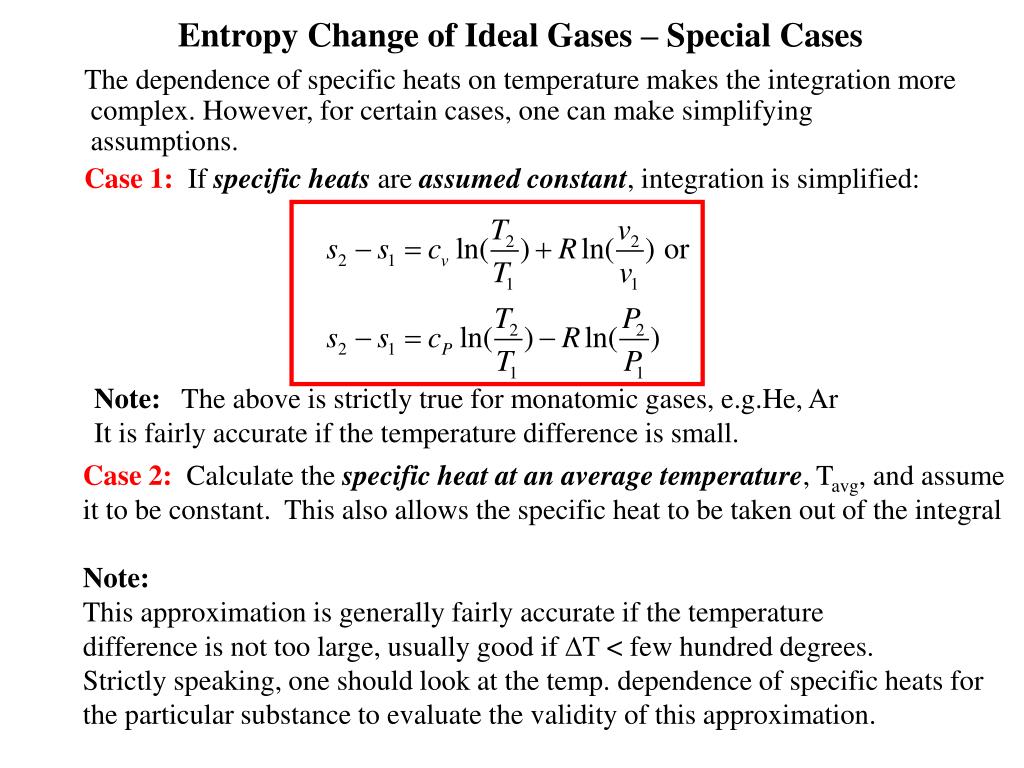
The change in free energy, \(\Delta G\), is equal to the sum of the enthalpy plus the product of the temperature and entropy of the system. Because both of system and environment return to their initial states when cycle is completed. For a reversible cycle, world entropy change is zero. The extreme case is that of a double-headed coin that never comes up tails, or a double-tailed coin that never results in a head. Entropy is a thermodynamic quantity that is generally used to describe the course of a process, that is, whether it is a spontaneous process and has a probability of occurring in a defined direction, or a non-spontaneous process and will not proceed in the defined direction, but in the reverse direction. The total change in internal energy of a system and the surroundings (the universe) is zero, that is Utot 0 U t o t 0. Gibbs free energy, denoted \(G\), combines enthalpy and entropy into a single value. Net entropy change means entropy change of the world (world means system plus environment). So if we want to calculate the entropy change S, we can arbitrarily choose some. Entropy, then, can only decrease from the value associated with uniform probability. Recall that entropy, which is defined as qrev/T, is a property of state.
Uniform probability yields maximum uncertainty and therefore maximum entropy. If there is heat Q absorbed by the reservoir at temperature T, the change in. H ( X ) := − ∑ x ∈ X p ( x ) log p ( x ) = E, Consider a system in contact with a heat reservoir during a reversible process.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
